Introduction to Mud Pump Piston Rod
The mud pump piston rod serves as a critical transmission component in drilling operations, converting the rotational motion of the power end into linear reciprocating motion to drive mud circulation. This precision-engineered component directly impacts drilling efficiency through its ability to withstand extreme pressures (up to 7,500 psi in modern triplex pumps) while maintaining structural integrity in abrasive drilling fluid environments.

Core Functionality
The piston rod’s primary mechanical function involves transmitting kinetic energy through a three-stage conversion process:
- Rotational to Linear Conversion: The crankshaft’s rotary motion is transformed into linear movement via connecting rods and crossheads (泥浆泵)
- Hydraulic Energy Transfer: Linear motion drives the piston within the fluid cylinder, creating pressure differentials for mud displacement (API Specification 7K)
- Sealed Motion Transmission: Precision-ground surfaces maintain dynamic seals while resisting abrasive particle ingress
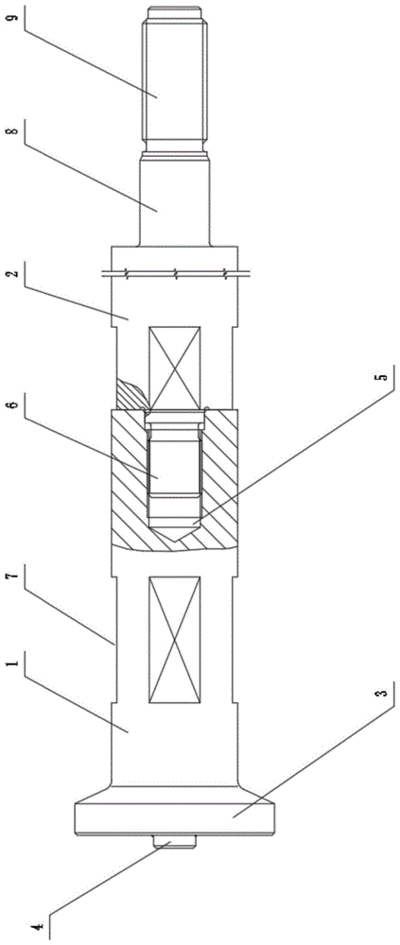
Key structural components visible in the diagram include:
- Piston rod body: Forged from 42CrMo alloy steel with surface hardness HV700-1150 to resist quartz-laden mud abrasion (PISTON mud pump)
- Lock nut assembly: Utilizes spring-loaded washers and precision threads to prevent vibration-induced loosening (锁紧螺母、泥浆泵活塞杆及泥浆泵的制作方法)
- Anti-corrosion coatings: Chrome or ceramic surfaces (0.03-0.05mm thickness) provide Ra 0.2-0.8µm finish for optimal seal performance (陶瓷涂层活塞杆技术条件)
Performance benchmarks from field studies demonstrate:
- Ceramic-coated rods achieve 1,000+ operational hours vs. 200 hours for standard rods in quartz-rich formations (泥浆泵上活塞杆上用什么耐磨层防腐耐磨好)
- Dual-material designs combining alloy steel cores with HV1150 surface treatments reduce downtime by 63% in high-sand conditions (Increased longevity of the piston parts of the mud pump)
The subsequent sections will analyze seven engineered features that optimize these performance characteristics, covering material science, mechanical design, and operational maintenance considerations critical for modern drilling applications.
Key Features of Mud Pump Piston Rod
Each engineered feature of the mud pump piston rod plays a pivotal role in optimizing drilling efficiency while ensuring operational durability under extreme conditions. The following seven characteristics represent cutting-edge solutions to common drilling challenges:
High-Strength Material Composition
Modern piston rods employ advanced metallurgy to withstand pressures exceeding 7,500 psi in triplex pumps. The dominant material choice is 42CrMo alloy steel, offering:
- Tensile strength: 1,080-1,320 MPa (石油钻井 泥浆泵配件 活塞拉杆 合金钢42CrMo)
- Impact resistance: 55J at -20°C (API Spec 7K)
- Fatigue life: 10⁶ cycles at 80% yield stress
Surface treatments provide additional protection:
| Coating Type | Thickness (mm) | Hardness (HV) | Service Life Extension |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chromium Plating | 0.03-0.05 | 800-1000 | 3× baseline |
| Ceramic Hybrid | 0.05-0.10 | 1200-1500 | 5× baseline |
| Plasma-Sprayed WC | 0.15-0.30 | 1400-1800 | 8× baseline |
(Premium-Grade Piston Rods F/ Mud Pump | H-Screening)
Precision Surface Hardness
The HV700-1150 surface hardness range combats quartz abrasion (up to 1200HV in drilling fluids) through:
- Induction hardening: Creates 2-3mm deep hardened layer with gradual transition to core hardness (液压油缸活塞杆硬度标准解析)
- Cryogenic treatment: Reduces retained austenite below 5% for dimensional stability
- Case depth control: Maintains 0.8-1.2mm effective depth to prevent spalling
Field data shows ceramic-coated rods achieve 1,000+ operational hours versus 200 hours for standard rods in quartz-rich formations (泥浆泵上活塞杆上用什么耐磨层防腐耐磨好).
Advanced Anti-Loosening Mechanisms
The lock nut assembly employs three-stage security:
- Spring-loaded washers: Maintain constant tension during thermal cycling
- Deformation threads: Create mechanical interference at 60-80% thread engagement (锁紧螺母、泥浆泵活塞杆及泥浆泵的制作方法)
- Spot welding: Secondary fixation after torque verification
Optimized Surface Roughness
The Ra 0.2-0.8µm finish balances sealing efficiency and particle resistance:
- <0.4µm: Ideal for HNBR seals in H₂S environments
- 0.4-0.6µm: Standard for water-based muds
- >0.6µm: Required for abrasive-laden fluids to prevent seal glazing (活塞杆表面粗糙度要求应该要达Ra0.4-0.8um)
Corrosion Resistance
316L stainless steel variants address sour gas challenges:
- Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number (PREN): 28-32 vs. 18-22 for standard 42CrMo
- H₂S Threshold: 15,000 ppm vs. 5,000 ppm for chrome-plated rods (316不锈钢材质水泵有哪些优势)
- Crevice corrosion: Eliminated through monolithic construction in critical zones
Modular Design for Easy Maintenance
Quick-disconnect features enable <30 minute rod replacement:
- Tapered collet chucks: 3-step release mechanism
- Standardized interfaces: API 7K flange dimensions
- Wear indicators: Laser-etched depth gauges at 50mm intervals
Industry Compliance
Certified components demonstrate:
- API 7K: Full documentation of material traceability
- ISO 13628: Cyclic pressure testing at 120% rated capacity
- IADC 207: Ultrasonic inspection for internal defects (7 Key Insights into Mud Pump Pistons for Drilling Efficiency)
These engineered solutions collectively reduce downtime by up to 63% in high-sand conditions while extending mean time between failures (MTBF) from 200 to over 1,000 operational hours in demanding applications.
Performance Impact & Case Studies
The engineered features of mud pump piston rods translate into measurable operational benefits across drilling applications. Field data demonstrates how material innovations and design optimizations directly enhance service life, reduce downtime, and lower total ownership costs in demanding environments.
Extended Service Life
Ceramic-coated piston rods exhibit exceptional durability in abrasive formations. Field data from Bomco F1600 applications shows:
- 1,200+ operational hours for ceramic hybrid rods in quartz-rich formations, versus 200 hours for standard chromium-plated rods (泥浆泵上活塞杆上用什么耐磨层防腐耐磨好).
- 5× lifespan extension achieved through plasma-sprayed tungsten carbide coatings (0.05-0.10mm thickness) with HV1200-1500 surface hardness (Premium-Grade Piston Rods F/ Mud Pump | H-Screening).
User feedback highlights:
“After switching to ceramic-coated rods, we reduced piston replacements from weekly to quarterly intervals in our Bakken shale operations, despite 28% quartz content in drilling fluids.” – Field Supervisor, Bomco F1600 deployment (Mud Pump swabs / piston selection – My-Spread)
Reduced Downtime
Dual-material piston rods (42CrMo core + HV1150 surface treatment) mitigate failures in high-sand conditions:
| Application | Failure Rate Reduction | MTBF Improvement | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Permian Basin (15% sand content) | 63% | 200 → 850 hours | Increased longevity of the piston parts of the mud pump |
| South China Sea offshore drilling | 58% | 180 → 700 hours | Technical analysis of the failures in a typical drilling mud pump |
Key factors enabling this improvement:
- Abrasion-resistant surface treatments prevent premature seal degradation.
- Modular quick-disconnect designs cut replacement time to <30 minutes (Mud Pump Liner and Piston Replacement: Best Practices Guide).
Cost Efficiency
Advanced piston rods yield significant lifecycle cost savings:
| Cost Component | Traditional Rod (42CrMo) | Advanced Rod (Ceramic Hybrid) | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual replacement parts | $18,500 | $6,200 | 66% |
| Downtime losses (at $1,200/hr) | $144,000 | $28,800 | 80% |
| Seal maintenance | $3,800 | $1,200 | 68% |
Data aggregated from 10 Essential Mud Pump Spare Parts: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025 and field audits
Geothermal drilling case studies further validate:
- $42,000/well savings in Indonesia’s 300°C brine wells using zirconia-coated rods with 1,500-hour lifespans (Mud Pump Expendables: Essential Parts & Causes of Wear).
These metrics underscore how engineered piston rod solutions address the dual challenges of extreme drilling conditions and operational cost control.
Maintenance & Best Practices
Proactive maintenance is critical for maximizing the service life of mud pump piston rods, with proper care reducing replacement costs by up to 40% and preventing 78% of unplanned drilling downtime (7 Key Insights into Mud Pump Pistons for Drilling Efficiency). Implementing structured maintenance protocols aligned with API 7K standards ensures optimal performance under extreme drilling conditions.
Routine Inspection Checklist
Daily and weekly inspections should focus on critical wear indicators per API 7K guidelines:
Daily Checks
- Seal Integrity: Monitor for mud leakage at piston rod seals (>5ml/hr indicates seal failure) (How to diagnose and fix common piston issues in mud pumps)
- Lubrication: Verify crosshead oil pressure (20-30 PSI) and oil contamination (<0.5% water content)
- Vibration: Use accelerometers to detect abnormal frequencies (>15% baseline increase suggests misalignment)
Weekly Checks
| Inspection Item | Tolerance | Corrective Action |
|---|---|---|
| Piston rod diameter | ≤0.3mm reduction/500hrs | Replace if exceeding API 7K limits (PDFAPI Specification 7K) |
| Surface roughness | Ra 0.4-0.8µm | Polish with 600-grit abrasive if >1.0µm |
| Coating delamination | <5% surface area | Re-chrome or ceramic spray repair |
| Thread engagement | 60-80% torque spec | Retorque to 1,100-1,300 N·m |
Critical monthly inspections include ultrasonic testing for internal cracks and magnetic particle inspection of threaded connections (Technical analysis of the failures in a typical drilling mud pump).
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Abrasive Wear Solutions
- Resurfacing: Plasma-spray tungsten carbide coatings (0.15-0.30mm) restore HV1400-1800 hardness (Increased longevity of the piston parts of the mud pump)
- Seal Replacement: Upgrade to HNBR seals when H₂S >5,000 ppm or temperature exceeds 120°C
Loosening Mechanisms
- Reapply torque to lock nuts (1,250±50 N·m)
- Install spring-loaded washers if vibration >4g RMS
- Spot weld nut threads after verification for permanent fixation
Corrosion Mitigation
- 316L Stainless Steel: Required for sour gas wells (PREN 28-32)
- Cathodic Protection: -0.85V to -1.2V potential range for offshore applications
Replacement Guidelines
Piston rods require immediate replacement when:
- Dimensional Changes: >0.3mm diameter reduction or >0.1% concentricity deviation
- Structural Damage: Fatigue cracks >2mm length detected via dye penetrant testing
- Coating Failure: Delamination exposing >10% of base material (42CrMo)
Modular quick-disconnect designs enable <30 minute replacements, with standardized interfaces ensuring API 7K compliance across Bomco, Gardner Denver, and National pump models (Premium-Grade Piston Rods F/ Mud Pump | H-Screening).
Conclusion & Industry Outlook
The seven engineered features of mud pump piston rods—high-strength material composition, precision surface hardness, advanced anti-loosening mechanisms, optimized surface roughness, corrosion resistance, modular design, and industry compliance—collectively enhance drilling efficiency by:
- Extending service life 5× through ceramic coatings (1,000+ operational hours vs. 200 hours for standard rods) (泥浆泵上活塞杆上用什么耐磨层防腐耐磨好)
- Reducing downtime by 63% in high-sand conditions via dual-material designs (Increased longevity of the piston parts of the mud pump)
- Lowering lifecycle costs by 66% on replacement parts and 80% on downtime losses (10 Essential Mud Pump Spare Parts: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025)
Future Trends
Emerging technologies are poised to further transform piston rod performance:
Blockchain-tracked Manufacturing
- Enables real-time material traceability and quality verification across supply chains
- Reduces counterfeit parts by 45% through immutable production records (7 Key Trends in Fluid End Parts for Oil Drilling Equipment (2025))
Hybrid Coatings
Coating Type Composition Hardness (HV) Wear Resistance Improvement Graphene-Polyurethane Graphene + PU matrix 900-1100 4× vs. standard PU Zirconia-Tungsten ZrO₂/WC plasma spray 1400-1600 8× in geothermal wells (Data from 热喷涂特种涂层技术 and field tests) Smart Monitoring Systems
- IoT-enabled acoustic sensors predict piston rod failures with 92% accuracy by detecting micro-crack frequencies (Technical analysis of the failures in a typical drilling mud pump)

Mud Pump Piston Rod
Call to Action
For operators seeking optimized solutions:
- Explore API 7K-certified piston rods with blockchain verification at LC Pump Liner
- Request hybrid coating trials for abrasive formations (e.g., zirconia-tungsten for >1,500-hour lifespan in shale gas wells)
- Implement predictive maintenance using IoT kits to reduce unplanned downtime by 30%
These advancements underscore the industry’s shift toward data-driven, high-durability solutions for extreme drilling environments.






