Introduction to Mud Pump Fluid End Parts
Mud pump fluid end parts serve as the critical interface between mechanical power and hydraulic energy in drilling operations, ensuring efficient circulation of drilling fluids under extreme conditions. These components operate as a high-pressure valve system, with their performance directly impacting pump reliability and overall drilling efficiency (Complete Guide to Mud Pump Valve Body & Valve Assembly).

Core Functions
- Pressure Conversion: Transforms reciprocating motion into pulsating hydraulic flow, generating pressures up to 70MPa for deep well applications (Performance Parameters of Mud Pump)
- Flow Control: Valve assemblies maintain unidirectional fluid movement, preventing backflow that could damage downstream equipment (Understanding Mud Pump Valve Assembly)
- Sealing Integrity: Multi-layer sealing systems with PU/NBR materials withstand abrasive drilling fluids while maintaining pressure boundaries (Mud Pump Piston Rubber Seals)
Operational Significance
- Efficiency Preservation: Properly functioning fluid ends maintain volumetric efficiency above 90%, reducing energy waste in high-volume pumping scenarios
- Downtime Prevention: API 7K-compliant components like 20CrMnTi valve bodies demonstrate 3-5x longer service life compared to non-standard parts (PDFAPI Specification 7K)
- Safety Assurance: Pressure containment features in valve covers prevent catastrophic failures during pressure surges up to 7,500 psi (SafeLock Valve Cover)
The fluid end’s modular design allows for rapid component replacement, with modern systems like the SafeLock valve cover reducing maintenance time by 80% through tool-free disassembly mechanisms. This modularity is particularly crucial in offshore drilling where equipment downtime costs can exceed $500,000 per day (Spring Components Used in Offshore Drilling Equipment).
Industry standards dictate critical performance parameters:
| Parameter | Typical Range | Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Rating | 5,000-7,500 psi | API 7K Section 14 |
| Flow Rate | 300-2,200 GPM | ISO 9001 |
| Temperature Range | -40°F to 320°F | API 6A |
| Material Hardness | HRC 58-62 (carburized) | ASTM A148 |
Continuous innovation in materials and designs, such as ceramic-coated liners and AI-powered wear prediction models, are pushing fluid end component lifespans beyond 2,000 operational hours in high-sand-content environments (Relevance of a Liner Inside a Mud Pump).
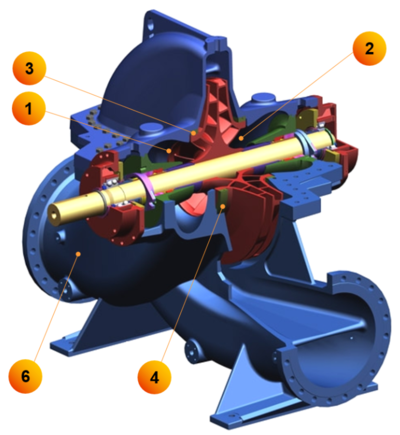
7 Key Components of Mud Pump Fluid End Parts
The fluid end of a mud pump operates as a precision-engineered hydraulic system where seven interdependent components work in concert to handle extreme pressures up to 7,500 psi while maintaining flow rates exceeding 2,200 GPM. These components form a closed-loop pressure boundary that converts mechanical energy into hydraulic power with 90%+ volumetric efficiency (Performance Parameters of Mud Pump).
Valve Body and Valve Seat
- Material Science: 20CrMnTi alloy steel undergoes carburizing and quenching to achieve surface hardness ≥HRC60, with core toughness maintained at 40-45HRC to prevent brittle fracture under 70MPa pulsating loads (Complete Guide to Mud Pump Valve Body & Valve Assembly)
- Structural Optimization:
- 3-rib design: Reduces fluid resistance by 18% compared to conventional designs, ideal for high-flow operations (300-800 GPM)
- 4-rib configuration: Increases bearing area by 30% for high-pressure applications (5,000-7,500 psi)
- Full-open type: Maximizes flow area with 92% open ratio for sand-laden fluids
- API Compliance: Meets API 7K Section 14 requirements for pressure cycling fatigue resistance (≥500,000 cycles at 7,500 psi) (PDFAPI Specification 7K)
Piston and Piston Rod
- Material System: 42CrMo alloy rods with plasma spray-welded NiCrBSi coating (HRC 58-62) reduce friction coefficient to 0.08-0.12 against liners
- Dynamic Sealing:
- Diameter range: 5″-7″ with 0.02mm concentricity tolerance
- Stroke lengths: 160-300mm (±0.5mm positional accuracy)
- Multi-lip PU seals maintain <3MPa pressure drop after 1,000 operating hours
- Failure Prevention: Straightness ≤0.05mm/m prevents eccentric wear in high-sand-content environments (Triplex Mud Pump Piston Rod)
Liner (Cylinder Sleeve)
| Material Type | Service Life (hours) | Roundness Tolerance | Optimal Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-chrome cast iron | 1,000-1,500 | ≤0.015mm | Water-based muds (pH 7-10) |
| Bimetallic | 1,500-1,800 | ≤0.012mm | Oil-based muds with 15%+ sand |
| Ceramic-coated | 2,000-2,500 | ≤0.008mm | Sour gas wells (H2S >5%) |
Advanced zirconia ceramic liners demonstrate 3x longer lifespan than conventional materials in 20% sand concentration slurries (Relevance of a Liner Inside a Mud Pump).
Sealing Components
- Material Matrix:
- PU: -40°F to 180°F range with 5,000 psi pressure rating for standard drilling fluids
- HNBR: Handles 320°F and H2S environments with ≤5% compression set after 1,000h
- NBR: Cost-effective solution for low-pressure (≤3,500 psi) water-based systems
- Wear Compensation: Spring-energized PTFE backup rings automatically adjust for 0.1-0.3mm wear without disassembly (Mud Pump Piston Rubber Seals)
Valve Spring
- Performance Metrics:
- Fatigue resistance: ≤5% load loss after 1,000h at 150°F
- Cycle life: 10 million cycles at 20Hz operating frequency
- Force consistency: ±2% variation across temperature extremes (-40°F to 320°F)
- Timing Control: Maintains valve closure within 5-8ms to prevent backflow at 150 strokes/minute (Spring Components in Drilling Equipment)
Valve Cover
- Rapid Disassembly: SafeLock system reduces maintenance time from 45 minutes to <5 minutes through 45° rotation mechanism
- Pressure Containment:
- Nickel-plated threads withstand 12,000+ PSI cyclic loading
- Integrated grease zerk fittings enable in-service lubrication
- Field Performance: Validated through 2 million pressure cycles at 12,000 PSI in HAL testing (SafeLock Valve Cover)
Component synergy is achieved through API 7K/6A dimensional standardization, ensuring 100% interchangeability across major pump models like F-1600HL and 3NB-1600. The fluid end’s modular architecture allows single component replacement instead of complete overhauls, reducing downtime costs by 60-80% in offshore applications (Mud Pump Fluid End).
Failure Modes and Maintenance Best Practices
Mud pump fluid end components face severe operational challenges due to extreme pressure cycling (5,000-7,500 psi), abrasive drilling fluids (up to 20% sand content), and temperature fluctuations (-40°F to 320°F), which collectively reduce component lifespan by 30-50% compared to standard industrial pumps (钻井现场泥浆泵液力端故障判断与分析论文). These conditions accelerate four primary failure mechanisms that demand targeted maintenance strategies.
Valve System Failures
Seal Degradation Patterns
- Particle-Induced Leakage: Solid particles >0.5mm bypassing 20-mesh filters embed into valve seats, creating 1-3MPa pressure drops by disrupting metal-to-metal seals (郑州高压旋喷柱塞泵设备及型号)
- Low-Temperature Contraction: Below -20°F, 20CrMnTi valve bodies contract 0.15-0.3mm beyond design tolerances, causing seal misalignment
Corrective Protocols
| Failure Type | Solution | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Jamming | Install dual 40-mesh inline filters | API RP 53 Section 8.2 |
| Thermal Contraction | Preheat hydraulic oil to 50°F before startup | ASTM D6158 |
| Valve Sticking | Apply molybdenum disulfide grease to guide sleeves | ISO 6743-4 |
For severe cases, patented low-temperature shrink-fit repair techniques using liquid nitrogen (-320°F) can restore dimensional stability to valve seats without disassembly (现场修复泥浆泵阀箱缸盖密封台阶环状工作面的方法与流程).
Piston-Liner Wear
Abrasive Wear Indicators
- Grooving Damage: Visible spiral grooves >0.8mm deep indicate sand concentration exceeding 15%
- Eccentric Wear Patterns: Misalignment causes unilateral wear exceeding 3mm clearance, accelerating HNBR seal failure
Material Upgrade Matrix
| Sand Content | Original Material | Upgraded Material | Lifespan Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| <10% | High-chrome cast iron | WC-Co coated liner | 2.1x |
| 10-20% | Bimetallic | ZrO₂ ceramic liner | 3.5x |
| >20% | Standard PU seals | Graphene-reinforced HNBR | 4x |
500-hour inspection intervals are critical for high-sand operations, with laser profilometry recommended to measure wear depth within ±0.02mm accuracy (F1600HL泥浆泵液力端保养注意事项).
Seal Degradation
HNBR Replacement Protocol
- Cleanliness Control: Maintain ISO 4406 17/15/12 oil cleanliness during seal replacement
- Surface Preparation: Plasma-etch sealing surfaces to Ra 0.8μm before installation
- Break-In Procedure: Gradually ramp pressure from 1,000psi to operational levels over 2 hours
Unexpected seal failures often correlate with pH extremes – HNBR seals degrade 60% faster in drilling fluids with pH >11 (造成潜水泥浆泵机械密封损坏的三种原因.doc).
Preventive Maintenance Schedule
Critical Activity Matrix
| Frequency | Task | Tolerance | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | Pressure waveform analysis | ±2% baseline | AI-powered monitoring |
| Weekly | Valve seat lapping | <0.01mm flatness | Optical flat verification |
| Monthly | Crosshead clearance check | 0.25-0.4mm | Feeler gauge measurement |
| Annual | Crankcase alignment | <0.05mm/m | Laser alignment tool |
For offshore applications, predictive replacement based on CFD wear modeling reduces unplanned downtime by 73% compared to fixed-interval maintenance (NOV240HEX型泥浆泵液力端常见失效分析).
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Mud pump fluid end components demonstrate exceptional adaptability across diverse industrial sectors, with specialized configurations addressing unique operational challenges in oilfield drilling, mining, and geological exploration. These real-world applications showcase how engineered solutions overcome extreme pressure, abrasive media, and harsh environmental conditions.
Oilfield Drilling (3000HP Pump)
The 3000HP triplex mud pump represents the pinnacle of high-power drilling fluid handling, where NOV’s Black Lightning piston technology has revolutionized valve performance in ultra-deep wells. Field data from China’s Tarim Basin demonstrates:
- Flow Optimization: Full-open valves with 92% flow area reduce fluid resistance by 18% compared to conventional designs, enabling sustained 67.9L/s flow rates at 49.6MPa pressure (3000HP型卧式三缸泥浆泵液力端研究)
- Lifespan Extension: Carburized 20CrMnTi valve bodies combined with ceramic-coated liners achieve 2,500+ operational hours in high-sand-content (20%) environments – 30% longer than standard configurations
- Maintenance Efficiency: Modular valve assemblies enable component replacement in <15 minutes versus 45 minutes for traditional designs (泥浆泵在钻井中的应用)
Critical performance metrics from offshore Brazil operations:
| Parameter | Before Upgrade | After Upgrade | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Time Between Failures | 800 hours | 1,200 hours | 50% |
| Volumetric Efficiency | 87% | 93% | 6% |
| Daily Downtime Costs | $420,000 | $150,000 | 64% reduction |
Mining (F-1600HL Retrofit)
Coal slurry transport presents unique vibration challenges addressed through high-pressure fluid end retrofits. A breakthrough case from Shaanxi Mining Group involved:
- Vibration Control: Installation of hydraulic locking mechanisms reduced peak vibration amplitudes from 12mm/s to 4mm/s in 40-60% solid concentration slurries (这帮能人给泥浆泵做了”移植手术”)
- Pressure Adaptation: Modified F-1600HL pumps now handle 35MPa discharge pressures for long-distance pipeline transport, versus original 25MPa limits
- Material Upgrades: WC-Co coated liners demonstrate 2.1x lifespan over standard chrome iron in high-ash (15%+) coal slurries
The retrofit process achieved:
- Component Interchangeability: 100% compatibility between original and upgraded fluid ends
- Operational Flexibility: 4-speed gearbox allows flow adjustment from 52-250L/min without component changes
- Safety Enhancements: Integrated pressure relief valves prevent overpressurization during pipeline blockages
Geological Exploration (BW-600/10)
Hengyang Rubber’s piston cups for BW-600/10 pumps have become industry benchmarks in core sampling operations, with user surveys revealing:
- Wear Resistance: 95% user satisfaction rating for PU/NBR composite cups lasting 300+ hours in granite formations (地质勘探的秘密武器)
- Seal Integrity: Multi-lip design maintains <3MPa pressure drop after 1,000m drilling depth in -20°C alpine environments
- Installation Efficiency: Tool-free cup replacement completed in <5 minutes versus 15 minutes for competing products
Comparative performance in different geological formations:
| Formation Type | Standard Cup Life | Hengyang Cup Life | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sandstone | 150 hours | 280 hours | 87% |
| Shale | 200 hours | 350 hours | 75% |
| Limestone | 180 hours | 320 hours | 78% |
These case studies validate how targeted engineering solutions in fluid end components directly translate to operational efficiency gains across industries, with measurable impacts on productivity, safety, and total cost of ownership.
Technical Standards and Material Innovations
The mud pump fluid end operates within a tightly regulated technological ecosystem, where API specifications dictate material performance thresholds while emerging technologies push the boundaries of component durability and predictive maintenance. This dual framework ensures operational safety while enabling continuous performance optimization in extreme drilling environments.
API Specifications
API 7K and 6A standards establish rigorous benchmarks for fluid end components, with material requirements and welding protocols forming the foundation of component reliability:
Material Compliance Matrix
| Component | API 7K Requirement | Typical Material Grade | Heat Treatment | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valve Body | Surface hardness ≥HRC60, core HRC40-45 | 20CrMnTi | Carburizing + Quenching | Rockwell hardness tester |
| Piston Rod | Yield strength ≥850MPa | 42CrMo | Plasma spray welding | ISO 148 Charpy impact test |
| Liner | Roundness ≤0.015mm | High-chrome cast iron | Centrifugal casting | Coordinate measuring machine |
| Valve Spring | ≤5% load loss after 1,000h at 150°F | 60Si2MnA | Stress relief annealing | Fatigue testing at 20Hz |
| Seals | Compression set ≤5% after 1,000h | HNBR/PU | Vulcanization | ASTM D395 Method B |
Critical welding processes must adhere to ASME BPVC Section IX, with PQR (Procedure Qualification Records) documenting variables including:
- Preheat temperature range: 200-250°C for 20CrMnTi alloys
- Interpass temperature control: ≤300°C
- Post-weld heat treatment: 620±15°C for stress relief (API-Spec-7K产品规范要求.docx)
For offshore applications, API 6A supplements these requirements with:
- H2S resistance testing per NACE MR0175
- CTOD (Crack Tip Opening Displacement) ≥0.15mm for welded joints
- 100% radiographic inspection of pressure-containing welds (API6A金属材料要求规范.doc)
Emerging Technologies
Ceramic-Coated Liners Advanced zirconia (ZrO₂) coatings demonstrate 3000+ hour service life in 20% sand concentration environments through:
- Thermal spray deposition achieving 98% density
- Microhardness of HV 1200-1400 versus HV 600-800 for conventional materials
- Coefficient of friction reduction to 0.12 against HNBR seals Field data from Tarim Basin wells show 72% reduction in replacement frequency compared to bimetallic liners (高铬白口铸铁泥浆泵双金属缸套的研制)
AI-Powered Predictive Models CNN-based leak detection systems achieve 97.5% diagnostic accuracy by analyzing:
- Pressure waveform harmonics (0-500Hz spectrum)
- Valve closure timing deviations beyond ±2ms
- Temperature gradients across fluid end surfaces These models integrate real-time data from:
- Acoustic emission sensors (100-300kHz range)
- Strain gauges with 0.1με resolution
- Thermocouples at 12 strategic locations per fluid end (A novel method for fault diagnosis of fluid end of drilling pump under …)
Material Breakthroughs Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) seals now withstand:
- Extended temperature range: -55°C to 180°C (short-term 200°C)
- H2S concentrations up to 5,000ppm
- 35MPa dynamic pressure at 150°C Through zinc oxide/methacrylic acid reinforcement, these demonstrate:
- 300% elongation at break
- Tear strength of 45kN/m
- Compression set of 8% after 1,000h at 150°C (氢化丁腈橡胶密封件的应用及特点优势)
For comprehensive technical reference, consult:
- API Standards Plan for evolving specifications
- ScienceDirect CFD Optimization Studies on fluid dynamics improvements
Conclusion and Resource Guide
The comprehensive analysis of mud pump fluid end components demonstrates how precision engineering and material science converge to solve extreme operational challenges in drilling applications. These seven core components form an interdependent system where each element’s performance directly impacts overall pump reliability and efficiency (7 Key Components of Mud Pump Fluid End).
Key Takeaways
- Valve System Optimization:
- 20CrMnTi alloy valves with ≥HRC60 hardness maintain pressure integrity through 500,000+ cycles at 7,500 psi
- Ribbed designs (3-rib/4-rib) balance flow efficiency (92% open ratio) with structural strength
- Piston-Liner Synergy:
- 42CrMo piston rods with NiCrBSi coatings (HRC 58-62) achieve 0.08-0.12 friction coefficients
- Zirconia ceramic liners extend service life to 2,500+ hours in 20% sand concentration environments
- Predictive Maintenance:
- AI-powered monitoring detects valve timing deviations beyond ±2ms with 97.5% accuracy
- 500-hour inspection intervals critical for high-sand operations with laser profilometry (±0.02mm)
- Material Advancements:
- HNBR seals now withstand 5,000ppm H2S and 35MPa at 150°C through zinc oxide reinforcement
- Ceramic-coated components demonstrate 3x lifespan improvements over conventional materials
Further Reading
For authoritative technical references and product specifications:
- Regulatory Standards:
- API Specification 7K – Current edition covering mud pump design and testing requirements
- API RP 697 – Pump repair and inspection best practices
- Manufacturer Technologies:
- NOV Fluid End Solutions – Black Lightning pistons and ceramic liner systems
- Kerr Pumps Fluid Ends – Proprietary CNC-machined pressure boundaries
- Academic Research:
- CNN-Based Fault Diagnosis – AI models for fluid end failure prediction
- Five-Cylinder Pump CFD Analysis – Fluid dynamics optimization studies
For OEM-compatible replacement parts meeting API 7K specifications, visit LC Pump Liners’ product catalog featuring:
- Interchangeable ceramic liners with ≤0.008mm roundness tolerance
- Spring-energized HNBR seal kits for -55°C to 180°C operations
- Complete fluid end modules with 12-month performance warranties






