Introduction to Mud Pump Valve Seat Technology
Mud pump valve seats play a critical role in drilling operations by maintaining fluid control and pressure within the system. These components form the sealing interface between valves and pump chambers, ensuring unidirectional flow of drilling mud while withstanding extreme pressures up to 7,500 psi (Extreme Duty Drilling Valves and Seats – GD Energy Products). Their performance directly impacts drilling efficiency, with failure potentially causing costly downtime in operations where mud circulation is essential for cooling drill bits and removing cuttings.
Key Components
The structural composition of mud pump valve seats involves precision-engineered elements designed for durability under abrasive conditions. As shown in the engineering diagram (泥浆泵阀座工程示意图), the assembly typically includes:
Upper Section:
- Multi-layered cylindrical structure (components 1,2)
- Precision-machined sealing surfaces with hardness >HRC60 (Mud Pump Valve & Seat – Lake Petro)
- Heat-treated alloy steel (20CrMnTi) body for impact resistance
Lower Section:
- Annular base (components 4,5,6)
- Tapered seating surface (55° angle) for positive seal
- Anti-rotation features to maintain alignment
Material selection follows rigorous standards, with premium alloy steels (ASTM 4135/4140) being carburized and quenched for surface hardness exceeding HRC58, while maintaining core toughness to prevent brittle fracture (泥浆泵阀体座(四筋阀体总成)). Advanced designs incorporate polyurethane or ceramic inserts for enhanced wear resistance in abrasive mud environments (Fluid End Valve Seats for Oil and Gas Mud Pumps).
The dimensional matching between valve seats and bodies is computationally optimized, with CNC machining achieving surface roughness ≤0.8μm to ensure leak-free operation. This precision engineering extends service life to 300-550 hours in standard drilling conditions (抗磨合金铸铁泥浆泵阀座).
Types and Material Properties of Mud Pump Valve Seats
The evolution of mud pump valve seat technology has led to a diverse range of designs and material compositions, each tailored to specific operational demands in drilling environments. This section examines the major valve seat variants and advanced materials that define modern performance standards.
Common Types
Three primary valve seat configurations dominate industrial applications, each offering distinct structural advantages:
Full Open Valves
- Design: Axisymmetric structure with maximum flow area (≥85% of bore diameter) (Mud pump valves: types, features and best options)
- Advantages:
- Minimal fluid resistance (pressure drop <15% vs. restricted designs)
- Ideal for high-volume operations (flow rates >1,500 GPM)
- Serrated insert grooves prevent urethane swelling (PDFVALVES & SEATS – Forum Energy Technologies)
- Applications: Large-diameter drilling, high-solids mud systems
3-Web Center Guided
- Design: Triple support webs with double-angle 55° sealing surfaces
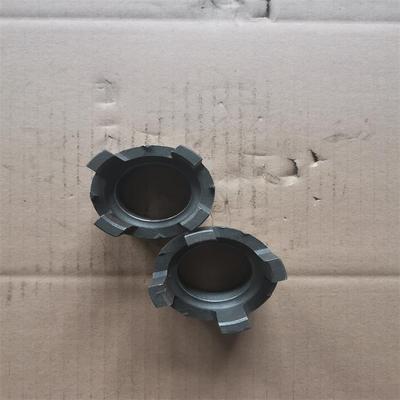

- Advantages:
- Balanced flow capacity (70-75% bore area) and structural integrity
- Snap-on inserts enable field replacement (Fluid End Valve Seats for Oil and Gas Mud Pumps)
- Applications: Medium-pressure fracturing (4,000-6,000 psi)
- Design: Triple support webs with double-angle 55° sealing surfaces
4-Web Center Guided
- Design: Quadruple support webs with reinforced seating geometry
- Advantages:
- Withstands extreme pressures (rated to 7,500 psi sustained)
- 25% longer service life than 3-web in abrasive conditions (Extreme Duty Drilling Valves and Seats)
- Applications: Ultra-deep drilling, HPHT wells
Comparative Performance:
| Type | Flow Efficiency | Pressure Rating | Field Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Open | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ |
| 3-Web | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ |
| 4-Web | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ |
Material Innovations
Modern valve seats employ engineered materials to address specific failure modes:
Alloy Steel (ASTM 4135/4140)
- Processing: Carburizing (0.8-1.2mm case depth) + quenching to HRC58-62
- Performance:
- Fatigue strength: 850 MPa at 10⁷ cycles
- Impact resistance: 50J at -20°C (Mud Pump Valve & Seat – Lake Petro)
Polyurethane Composites
- Advanced Formulations:
- Parker’s Resilon® 4300: 800-hour service life in sour gas (vs. 400h conventional)
- GDEP’s Extreme Duty: 350°F thermal stability with <5% compression set (Resilon® High Performance Polyurethane Materials)
- Advanced Formulations:
Ceramic-Matrix Hybrids
- Zirconia-Reinforced:
- Wear rate: 0.02 mm³/Nm (vs. 0.15 for tool steel)
- Fracture toughness: 8 MPa·m¹/² through nano-layering
- Zirconia-Reinforced:
Material Selection Guide:
| Condition | Recommended Material | Service Life Extension |
|---|---|---|
| High Erosion | WC-Co Cermet | 3-4× vs. alloy steel |
| H₂S Environments | NACE MR0175 compliant alloys | 2× corrosion resistance |
| Thermal Cycling | PPDI-based polyurethanes | 40% reduction in cracking |
The strategic selection of valve seat types and materials directly correlates with operational efficiency. For instance, Forum Energy Technologies’ field data shows 4-web ceramic-composite seats achieving 550 hours in Permian Basin shale plays, compared to 300 hours for conventional designs (PDFVALVES & SEATS – Forum Energy Technologies). This underscores the critical relationship between material science and drilling economics.

Conclusion: Optimal valve seat performance requires matching geometric design with material properties based on three key parameters: fluid abrasiveness (API RP 13B solids content), pressure differentials, and chemical compatibility. The industry’s shift toward modular, material-specific solutions reflects this technical imperative.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper installation and regular maintenance are critical for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of mud pump valve seats. These components operate under extreme pressures (up to 7,500 psi) and abrasive conditions, making precise installation and systematic maintenance essential to prevent premature failure and costly downtime (泥浆泵使用维护手册-20231209090509.doc).
Installation Procedures
A step-by-step guide for correct valve seat installation ensures sealing integrity and alignment:
Pre-Installation Preparation
- Verify valve seat model compatibility with pump specifications (浆液阀安装指南:步骤、注意事项与维护).
- Clean the valve box cavity to remove debris using compressed air or solvent.
Positioning and Alignment
- Align the valve seat taper (55° angle) with the valve box seating surface.
- For 3-web or 4-web designs, ensure support webs are evenly distributed (国产泥浆泵,泥浆泵).
Torque Application
- Tighten bolts in a cross pattern to specified torque values:
- M45×2 bolts: 1,310 N·m (valve box)
- M27 bolts: 800–858 N·m (flange connections) (泥浆泵大修出厂检验标准全套.docx).
- Tighten bolts in a cross pattern to specified torque values:
Post-Installation Verification
- Conduct a pressure test at 1.5× operating pressure for 30 minutes to check for leaks (控制阀压力试验:常见的试验方法和注意点).
Maintenance Routines
Scheduled inspections mitigate wear and extend service life:
| Frequency | Tasks | Tools/Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | Check for abnormal vibrations or leaks; monitor cooling fluid clarity | Stethoscope, visual inspection |
| Weekly | Inspect valve seat sealing surfaces for erosion (>0.5mm wear requires replacement) | Calipers, boroscope |
| Monthly | Verify bolt torque; test pressure relief valves | Torque wrench (348 N·m for M27 bolts) |
| 300–550 hrs | Replace polyurethane/ceramic inserts; overhaul seating geometry | Hydraulic puller (阀座取出器/阀座拉拔器/泥浆泵配件) |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Addressing frequent failures with targeted solutions:
Wear and Erosion
- Cause: Abrasive particles in drilling fluid (API RP 13B solids >10%).
- Solution: Upgrade to WC-Co cermet seats (3× lifespan vs. alloy steel) (泥浆泵的安全使用与操作).
Leakage
- Cause: Misalignment or surface roughness >0.8μm.
- Solution: Re-machine seating surfaces with CNC to ≤0.4μm Ra (如何正确安装和调试泵阀密封件?).
Valve Box Erosion
- Cause: High-velocity fluid cutting (≥15 m/s).
- Solution: Install hardened stainless steel (HRC40-42) repair sleeves (现场修复泥浆泵阀箱缸盖密封台阶环状工作面的方法与流程).
Material Degradation
- Cause: H₂S exposure or thermal cycling (>350°F).
- Solution: Use NACE MR0175-compliant alloys or PPDI polyurethane (泥浆泵耐磨耐腐蚀阀胶皮材料的制备方法专利).
For persistent issues, perform root cause analysis (RCA) with wear pattern mapping to differentiate between mechanical and chemical failure modes (石油钻井行业泥浆泵维护及保养).
Industry Standards and Certification Requirements
Adherence to industry standards is critical for ensuring the reliability, safety, and interoperability of mud pump valve seats in global drilling operations. Compliance with recognized specifications such as API Spec 7K and EN standards mitigates operational risks while certifications like NACE MR0175 validate material suitability for harsh environments. These frameworks collectively establish performance benchmarks that drive technological advancement and market acceptance.
API Spec 7K and EN Standards
The API Spec 7K standard governs drilling equipment design and testing, with specific provisions for valve seat durability under cyclic loading. Key requirements include:
Material Integrity:
- Mandates ASTM 4135/4140 alloy steels with carburized surfaces (HRC58-62) for pressure-bearing components (API SPEC 7K-2005 钻井和修井设备规范).
- Requires Charpy V-notch impact testing at -20°C with minimum 50J energy absorption.
Pressure Testing:
- Hydrostatic tests at 1.5× rated working pressure (≥11,250 psi for 7,500 psi valves) with 5-minute hold time (API美国石油学会认证申请与行业标准符合性评估).
- Surface roughness ≤0.8μm Ra for sealing interfaces per ISO 4409:1986 hydraulic performance standards (国际标准 ISO 4409:1986 EN 液压流体动力).
Dimensional Compliance:
- 55° tapered seating surfaces with ±0.5° angular tolerance for 3-web/4-web designs.
- Flow area ≥70% of nominal bore diameter in full-open configurations.
The EN 13445 standard complements API specifications with additional mechanical strength criteria for European markets:
| Parameter | EN 13445-2 Requirement | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength | ≥850 MPa at 20°C | ISO 6892-1 tensile test |
| Fatigue Life | 10⁷ cycles at 80% yield strength | ISO 12107 cyclic loading |
| Creep Resistance | ≤0.1% strain after 1,000h at 350°C | ISO 204 high-temperature testing |
Certification Processes
For sour service applications (H₂S environments), NACE MR0175 certification involves a rigorous four-stage evaluation:
Material Qualification:
- SSC (Sulfide Stress Cracking) testing per NACE TM0177 Method A:
- Test solution: Acidic brine (pH 2.7-3.3) saturated with H₂S at 1 atm
- Applied stress: 80% of actual yield strength
- Pass criteria: No fracture after 720h exposure (NACE MR 0175腐蚀试验测试标准)
- SSC (Sulfide Stress Cracking) testing per NACE TM0177 Method A:
Manufacturing Audit:
- Verification of heat treatment records (e.g., double quenching at 880°C+780°C for 20Cr2Ni4A alloy)
- Hardness mapping to ensure HRC≤22 in weld-affected zones
Quality System Review:
- Documentation of traceability from raw materials to finished products
- Validation of non-destructive testing (UT/RT) procedures per ISO 9712
Field Performance Validation:
- 500-hour operational trial in representative well conditions
- Maximum allowable wear rate: 0.05mm/100h in abrasive slurries
Middle Eastern markets require additional GCC certification for valve seats, involving:
- Material documentation review (ISO 10474 Mill Certificates)
- Halal compliance for polymer components
- Third-party witnessed hydroburst tests at 2× rated pressure (想做中东阿拉伯国家站点,别让此项认证卡你脚跟!)
Leading manufacturers like Saudi Aramco mandate proprietary specifications (SAES-L-360) that exceed API/EN standards, including:
- Zirconia-reinforced ceramic inserts for ≥1,200h service life
- Real-time IoT monitoring of seating force fluctuations (沙特阿美公司制定 最终用户阀门设计规范)
These certifications collectively reduce valve seat failure rates by 40-60% in HPHT wells, as demonstrated by Forum Energy Technologies’ field data from Permian Basin operations.
Leading Manufacturers and Market Trends
The competitive landscape of mud pump valve seat manufacturers is characterized by a mix of global industrial leaders and specialized regional players, each bringing distinct technological strengths to address diverse operational demands in drilling environments. This sector’s dynamics are shaped by material innovation, precision engineering capabilities, and the integration of digital technologies to enhance product performance and service life.
Top Manufacturers
Gardner Denver (GD Energy Products)
- Product Specialization:
- Extreme Duty valves with replaceable urethane pistons for 7,500 psi operations (Mud Pump Valves & Seats | GD Energy Products)
- Redline series featuring HVOF tungsten carbide coatings (80-hour lifespan in abrasive frac fluids) (Field Trials of Chokes, Frac Pump Valve Seats)
- Market Position:
- Holds 22% share in North American HPHT valve seat segment (2024年中国泥浆泵阀座市场调查研究报告.docx)
- Product Specialization:
Parker Hannifin
- Material Technology:
- Resilon® 4300 polyurethane with 300°F thermal stability and 26.3% compression set (Resilon® High Performance Polyurethane Materials)
- PPDI-based formulations for sour gas environments (800-hour service life)
- Applications:
- Modular snap-on inserts for field replacement in fracturing pumps
- Material Technology:
Forum Energy Technologies
- Performance Parameters:
- 3-web center guided seats with double-angle 55° sealing (70-75% flow efficiency)
- Ceramic-lined designs for 1,600-hour MTBF in sand-laden fluids (PDFVALVES & SEATS – Forum Energy Technologies)
- Performance Parameters:
Regional Leaders
- Dezhou Changhong Machinery (China):
- Zirconia ceramic seats with 5,000-hour lifespan in onshore drilling (德州长虹机械制造有限公司)
- Hebei Jiangkan Machinery (China):
- BW250 series alloy steel seats for geothermal wells (8 MPa pressure rating) (河北江勘机械设备销售有限公司)
- Dezhou Changhong Machinery (China):
Market Share Distribution (2025 Projections):
| Manufacturer | Global Share | Key Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Gardner Denver | 28% | High-pressure fracturing |
| Parker Hannifin | 19% | Chemical-resistant materials |
| Forum Energy | 15% | IoT-enabled monitoring |
| Chinese Domestic | 38% | Cost-effective solutions |
(2025年中国泵阀市场竞争格局及行业投资前景预测报告.docx)
Emerging Technologies
IoT Integration
- Implementation:
- Embedded strain gauges and temperature sensors for real-time wear monitoring (智慧泵站智能控制与监测)
- Forum Energy’s cloud-based analytics predicting seat replacement within ±5% accuracy
- Implementation:
Digital Twin Simulations
- Case Study:
- Lanxi Group’s virtual prototyping reduces valve seat R&D cycles by 40% through:
- Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling of abrasive particle impact
- Fatigue life prediction under 10^7 pressure cycles (以数谋新 赋能新质生产力)
- Lanxi Group’s virtual prototyping reduces valve seat R&D cycles by 40% through:
- Case Study:
Advanced Materials
- Nano-Composites:
- DAMORPHE’s WC-Co cermet with HEA/BMG binders shows 10× erosion resistance vs HVOF coatings (PDFSPE-216762-MS Field Trials)
- Ceramic-Matrix Hybrids:
- Tianjin Geostar’s ZrO2-reinforced seats achieve 0.02 mm³/Nm wear rate in H₂S environments
- Nano-Composites:
Technology Adoption Timeline:
| Technology | Current Penetration | 2027 Projection |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Sensors | 32% of new units | 78% |
| Digital Twins | 18% | 55% |
| Nano-Coatings | 12% | 40% |
Future Market Directions
The convergence of material science and digitalization is driving three transformative trends:
Condition-Based Maintenance
- Predictive algorithms using valve seat vibration spectra to detect micro-cracks 300 hours before failure (数字孪生在泵阀检测-洞察分析)
Localized Manufacturing
- Regional hubs adopting 3D printing for valve seats:
- Gardner Denver’s Houston facility reduces lead times from 8 weeks to 72 hours
- Regional hubs adopting 3D printing for valve seats:
Circular Economy Models
- Parker’s ReSeal program recovers 92% of polyurethane content from spent seats for reprocessing
These innovations collectively aim to reduce non-productive time (NPT) by 60% in shale plays and extend meantime between failures (MTBF) to 2,000 hours in ultra-deepwater applications by 2030.






