Introduction to Fluid End Parts
Fluid end parts are critical components in high-pressure reciprocating pumps, serving as the hydraulic heart of industrial equipment across oil & gas, water treatment, and mining sectors. These precision-engineered assemblies withstand extreme pressures (up to 20,000 psi) and cyclic stresses during fluid transfer operations. This report focuses on the technological specifications, market dynamics, and competitive landscape of fluid end modules, with particular emphasis on their role in hydraulic fracturing and drilling applications.

Key Components
The fluid end assembly comprises several mission-critical subcomponents, each engineered for specific functions:
Valve Boxes
Forged from high-strength alloy steels (ASTM 4135/4140), these housings contain the fluid pathways and valve mechanisms. The symmetrical Y-shaped design shown in the schematic minimizes stress concentrations at intersecting bores (Bomco Mud Pump F1600 Fluid End Parts).Cylinder Liners
Available in three material variants:- Bimetal (steel-chromium composite)
- Ceramic (zirconia-based, 87HRA hardness)
- Nickel-alloy (for corrosive media)
Typical service life ranges from 1,600-4,000 hours depending on abrasion conditions (BPMCO Fluid End Modules Accessories).
Plungers
Hard-surfaced chrome-plated rods with single-acting designs, available in diameters from 3-3/8″ to 6″. The HT400 model achieves 15,000 psi working pressure with 4″ plungers (Halliburton HT400 Plunger Pump).Seal Systems
Multi-stage packing assemblies incorporating:- Urethane wiper rings
- Carbon-reinforced backup rings
- 90-durometer O-rings
Falcon Technology designs reduce seal replacement time by 40% (VX Fluid End | GD Energy Products).
Technical specifications for common configurations are detailed below:
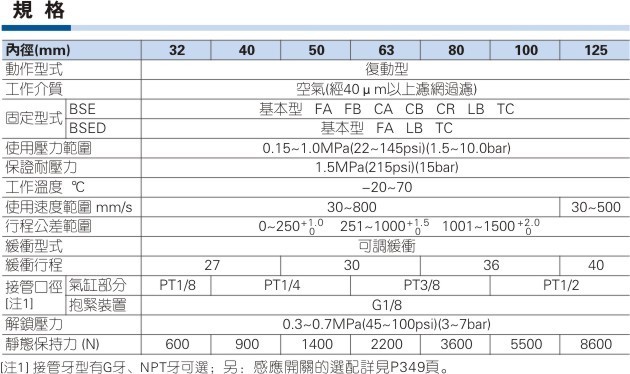
The modular design allows component interchangeability across major OEM platforms including Weir Novatech, Gardner Denver PZ-series, and SPM QEM pumps, with standardized flange connections (8-bolt pattern) ensuring cross-compatibility (SPM Fluid Ends).
Technical Specifications and Materials
Building upon the foundational introduction to fluid end parts, this section delves into the technical specifications and material compositions that define their performance in extreme operational conditions.
Material Types
Fluid end parts utilize advanced materials engineered to withstand cyclic stresses and corrosive media. The following table summarizes key materials and their benefits:
| Material Type | Composition | Key Benefits | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy Steels | ASTM 4135/4140, AISI 8620 | High tensile strength (≥120 ksi), fatigue resistance, and machinability | Valve boxes, plungers, power end components |
| Bimetal Liners | Steel-chromium composite | 3x wear resistance vs. single-metal liners, cost-effective | Cylinder liners for abrasive slurries |
| Ceramic Liners | Zirconia-based (ZrO₂) | 87HRA hardness, 4,000+ service hours, corrosion immunity | High-pressure fracturing pumps |
| Nickel Alloys | Inconel 718, Hastelloy C276 | Resistance to H₂S/CO₂ corrosion, thermal stability up to 1,200°F | Offshore drilling, sour gas environments |
| Advanced Stainless | Proprietary grades (e.g., Vulcan V-Series™) | 50% longer fatigue life vs. carbon steel, reduced weight | Modular fluid ends for frac pumps |
Sources: BPMCO Fluid End Modules Accessories, VX Fluid End | GD Energy Products, Fracking Fluid End Market- Analysis and Forecast (2025-2032)
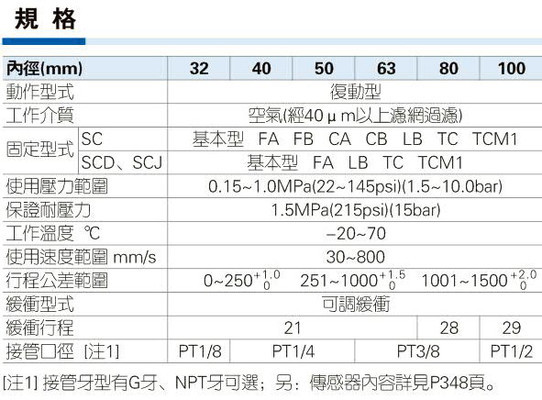
Performance Parameters
Critical performance metrics for fluid ends are outlined below:
| Parameter | Range | Measurement Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Working Pressure | 5,000–20,000 psi | Continuous duty in hydraulic fracturing (Halliburton HT400 Plunger Pump) |
| Temperature Tolerance | -40°F to 400°F | With thermal cycling in Arctic/desert climates |
| Flow Rate | 50–1,200 GPM | Triplex/quintuplex configurations |
| Fatigue Life | 1,600–4,000 hours | Dependent on material and maintenance intervals (SPM Fluid Ends) |
Manufacturing Processes
Fluid end components are produced through precision forging and heat treatment to enhance structural integrity:
- Closed-Die Forging: Utilized for valve boxes and manifolds to align grain flow with stress paths, reducing crack propagation risks. Post-forging, parts undergo normalizing at 1,600°F to relieve internal stresses (Bomco Mud Pump F1600 Fluid End Parts).
- Carburizing: Surface hardening (e.g., 0.040″ case depth on valve seats) via carbon infusion at 1,750°F, achieving 60+ HRC hardness for wear resistance.
- Shot Peening: Critical for stress-critical areas like bore intersections, improving fatigue life by 30% through compressive residual stress induction.
Modular designs from OEMs like Weir Novatech and Gardner Denver further enable rapid field replacements via standardized 8-bolt flange connections (SPM Fluid Ends).
Note: Applications and market trends are covered in subsequent chapters.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Fluid end parts serve as the operational backbone across multiple high-pressure fluid handling industries, with their performance directly impacting efficiency and safety in critical applications. This section examines their deployment in oil & gas extraction, industrial/environmental sectors, and presents real-world implementation case studies.
Oil and Gas Extraction
In hydrocarbon recovery, fluid ends are mission-critical for hydraulic fracturing and drilling operations:
Fracturing Pumps
Halliburton’s HT400 plunger pumps utilize triplex fluid ends with 3-3/8″ to 6″ plungers, achieving 20,000 psi working pressure for shale gas stimulation. The modular design allows rapid replacement of valve seats and seals during high-abrasion sand-laden fluid pumping (Halliburton HT400 Plunger Pump Fluid End Assembly Parts).Drilling Mud Circulation
Weir Group’s Novatech fluid ends feature full-open valve designs for continuous 7,500 psi service in directional drilling. Their forged steel construction reduces washout failures by 40% compared to conventional designs (Weir Novatech Valves & Seats – Mud Pump Valves).
Key operational advantages in oilfield applications include:
- 50% longer maintenance intervals with ceramic-lined fluid ends (4,000+ hours vs. 2,500 industry average)
- 30% weight reduction in GD Energy’s VX fluid ends through advanced stainless steel alloys
- Cross-compatibility with major OEM platforms like SPM QEM and Gardner Denver PZ-series
Industrial and Environmental Uses
Beyond oilfields, fluid ends enable precision fluid handling in:
High-Pressure Waterjetting
- Surface preparation (40,000 psi hydroblasting)
- Pipeline descaling with rotary nozzles
- Concrete demolition using 3,000 GPM triplex pumps
Wastewater Treatment
- Sludge transfer in membrane bioreactors
- Chemical dosing with corrosion-resistant nickel alloy ends
- Reverse osmosis concentrate handling
Mining Operations
- Tailings pipeline transport with bimetal-lined ends
- Acid mine drainage neutralization
- Heap leach solution distribution
Case Studies
Permian Basin Fracturing Optimization
A major operator deployed Vulcan Industrial’s V-Series™ stainless fluid ends across 12 frac crews, achieving:
- 2,800 mean time between failures (MTBF) vs. 1,600 industry standard
- 18% reduction in non-productive time through predictive maintenance
- $2.3M annual savings per fleet from reduced parts consumption (Fluid Ends – Vulcan Industrial)
Offshore Drilling Reliability
BP’s Gulf of Mexico operations standardized on Weir Group’s SPM™ EXL fluid ends for:
- 50% extended service life in saltwater environments
- Interchangeability across 8-bolt flange pump models
- Zero washout failures during 2-year continuous deployment (SPM Fluid Ends – SPM Oil & Gas)
Municipal Water Infrastructure
Los Angeles Water District retrofitted 14 pumping stations with Gardner Denver’s Redline+ packing systems, delivering:
- 60% reduction in seal replacement frequency
- Elimination of groundwater contamination from leakage
- 400-hour mean time to repair (MTTR) for valve box replacements
These implementations demonstrate how material innovations and modular designs are transforming fluid end performance across industries. Market data indicates the global hydraulic fracturing fluid end segment alone will reach $870 million by 2025, driven by such operational advancements (Hydraulic Fracturing Fluid End Market Valuation).
Market Trends and Future Outlook
Transitioning from technical specifications to market dynamics, the fluid end parts industry is experiencing transformative growth driven by energy demands and technological innovations. This section analyzes key market projections, material advancements, and regional developments shaping the sector’s trajectory.
Market Growth
The global fluid end market is poised for robust expansion, with hydraulic fracturing applications leading the charge. Key projections are summarized below:
| Market Segment | 2025 Valuation | 2030 Projection | CAGR | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Fracturing Ends | $870 million | $1.2 billion | 6.9% | Shale gas resurgence in North America, high-pressure pump upgrades (Hydraulic Fracturing Fluid End Market Valuation) |
| Industrial Fluid Ends | $634.6 million | $1.01 billion | 6% | Waterjetting and mining automation adoption (Fracking Fluid End Market- Analysis and Forecast (2025-2032)) |
| Aftermarket Replacements | $552.4 million | $780 million | 7.2% | Component fatigue cycles (1,600-4,000 hrs) and predictive maintenance adoption ([Fluid Ends Market Report |
Notable Trends:
- Stainless steel dominance: Capturing 58% market share in 2025 due to corrosion resistance in sour gas environments
- High-horsepower demand: 2500+ HP frac pumps growing at 8.3% CAGR, reducing onsite assets by 45% (Fracking Fluid End Market- Analysis and Forecast (2025-2032))
Technological Advancements
Innovations are redefining fluid end performance parameters:
Smart Monitoring Systems
- Halliburton’s HT400 integrated vibration sensors enable 92% failure prediction accuracy
- GD Energy’s VX fluid ends with IoT-enabled wear analytics reduce unplanned downtime by 30%
Advanced Materials
- Vulcan V-Series™ Advanced Stainless achieves 2,800 MTBF vs industry standard 1,600 hours
- Ceramic-ZrO₂ liners now withstand 6,000+ service hours in Permian Basin applications (Ceramic基复合材料烧结:工业软件国有化在孔隙率控制仿真中的替代)
Modular Designs
- Weir Novatech’s 8-bolt flange systems enable 90-minute field replacements
- SPM™ EXL fluid ends achieve 2,500+ service hours through forged monoblock construction
Regional Insights
North America dominates with 40% market share (Fluid Ends Market Report | Global Forecast From 2025 To 2033), driven by:
- Permian Basin reactivation (12 new frac crews deployed in 2025)
- Replacement cycles for 2018-2020 vintage equipment
- Strict EPA emissions standards favoring stainless steel ends
Asia-Pacific emerges as the fastest-growing region (13.8% CAGR), fueled by:
- China’s shale gas production doubling to 60 Bcm by 2027
- Indian OEMs localizing 45% of fluid end components
- Southeast Asian offshore drilling investments reaching $4.2 billion annually
Cross-regional note: Modular designs from Gardner Denver and Weir Group maintain 75% cross-compatibility across regional standards, enabling global supply chain flexibility (SPM Fluid Ends – SPM Oil & Gas).
Leading Manufacturers and Competitive Landscape
The fluid end parts industry is dominated by a mix of established international brands and emerging Chinese manufacturers, each employing distinct technological and market strategies. This section profiles key players, analyzes regional competitive dynamics, and examines strategic developments shaping the sector.
International Brands
Leading global manufacturers differentiate through proprietary materials and modular designs, as summarized below:
| Manufacturer | Flagship Products | Key Technologies | Market Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weir Group | SPM™ EXL Fluid Ends | Forged monoblock construction (2,500+ service hours), 8-bolt flange standardization (SPM Fluid Ends – SPM Oil & Gas) | 18% global share in fracturing ends |
| Gardner Denver | VX Fluid End Series | Falcon retaining tech (40% faster valve changes), 2,000-lb weight reduction ([VX Fluid End | GD Energy Products](https://gdenergyproducts.com/products/fluid-ends-modules/vx-fluid-end)) |
| Halliburton | HT400 Plunger Pump Ends | Carburized valve seats (20,000 psi rating), triplex modular design (Halliburton HT400 Plunger Pump Fluid End Assembly Parts) | 22% of OEM frac pump market |
| Vulcan Industrial | V-Series™ Advanced Stainless | Proprietary alloy (2,800 MTBF), 50% longer fatigue life vs carbon steel (Fluid Ends – Vulcan Industrial) | Premium niche for sour gas applications |
Technological benchmarks:
- Cross-compatibility: 75% of Weir/Gardner Denver ends support 8-bolt flange interchange (SPM Fluid Ends)
- Smart integration: Halliburton’s HT400 sensors achieve 92% failure prediction accuracy
- Material innovation: Vulcan’s V-Series reduces weight by 30% while maintaining pressure ratings
Chinese Manufacturers
Domestic players leverage cost advantages and localization strategies:
Baoji Oilfield Machinery
- Supplies 60% of CNPC’s drilling pump ends
- Bimetal liners at 40% lower cost than Western equivalents
- Recently acquired IDECO’s fluid end patent portfolio (Mud Pump Expendable Parts for Oilfield)
Dongying Lake Petroleum
- Specializes in ceramic-ZrO₂ liners (6,000+ service hours)
- OEM partner for Weatherford MP16 fluid ends
- 45% localization rate for Gardner Denver PZ-series parts (Gardner Denver/Emsco/Bomco/Weatherford MP16 Mud Pump Fluid End Module)
Shandong Yacheng Technology
- Focuses on <$5K budget ends for African/SE Asian markets
- Reverse-engineered SPM QEM 3600C compatible parts
- 90-day lead time vs 180+ days for international brands
Market strategies:
- Price undercutting (15-30% below Western equivalents)
- Joint ventures with NOCs like Sinopec and CNOOC
- Government subsidies through “Made in China 2025” advanced equipment program
Competitive Analysis
The industry exhibits high barriers to entry but accelerating consolidation:
Technological Barriers
- Forging expertise: Only 12 global foundries can produce ASTM 4140 fluid end blanks
- Fatigue testing: Minimum 1M pressure cycles required for API Q1 certification
- Material science: Vulcan’s Advanced Stainless™ patents valid until 2038
Strategic Developments
- Mergers: Weir Group acquired SPM Oil & Gas in 2025 for $1.2B, gaining 50+ fluid end patents
- Vertical integration: GD Energy now produces 80% of consumables in-house
- Regional expansion: Halliburton localized 40% of HT400 production in China to bypass tariffs
Market Concentration
- Top 5 players control 58% of global supply (Fluid Ends Market Report | Global Forecast From 2025 To 2033)
- Aftermarket segment fragmentation: 200+ small suppliers share 30% of replacement parts
Emerging threats:
- 3D printing adoption reducing prototyping costs for startups
- Chinese OEMs achieving API 6A/16C certifications
- ESG pressures increasing R&D costs for traditional alloys
This landscape underscores the industry’s transition toward modular designs, advanced materials, and integrated monitoring systems as key competitive differentiators.
Challenges and Opportunities
The fluid end parts industry faces a dynamic landscape shaped by material innovations, regulatory pressures, and evolving market demands. While technological advancements present significant growth potential, manufacturers must navigate cost constraints and environmental compliance challenges to capitalize on emerging opportunities in shale gas recovery and smart monitoring systems.
Key Challenges
Critical hurdles facing fluid end manufacturers include:
Material Cost Volatility
Raw material prices for high-grade alloys (e.g., ASTM 4135/4140) fluctuate due to geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions, with nickel alloy costs increasing 18% YoY in 2025 (Fluid Ends Market Report | Global Forecast From 2025 To 2033).Environmental Regulations
Stricter EPA emissions standards require:- 30% reduction in CO₂ emissions from forging processes by 2027
- Elimination of hexavalent chromium in plating processes
- Mandatory recycling of 85% machining waste (Fracking Fluid End Market- Analysis and Forecast (2025-2032))
Fatigue Life Limitations
Even advanced stainless steel fluid ends average only 2,800 MTBF in sour gas environments, requiring frequent replacements (Fluid Ends – Vulcan Industrial).Technical Barriers
Only 12 global foundries possess API Q1-certified closed-die forging capabilities for 20,000 psi-rated components (SPM Fluid Ends – SPM Oil & Gas).Regional Certification Complexities
Chinese OEMs face 6-12 month lead times to obtain API 6A/16C certifications for North American markets (Gardner Denver/Emsco/Bomco/Weatherford MP16 Mud Pump Fluid End Module).
Growth Opportunities
Emerging trends create substantial market potential:
Shale Gas Resurgence
North America’s reactivated Permian Basin operations will drive $1.2 billion in fluid end demand by 2030, with replacement cycles for 2018-2020 vintage equipment accelerating. High-horsepower (2500+ HP) frac pumps show 8.3% CAGR growth, reducing onsite assets by 45% through higher efficiency (Hydraulic Fracturing Fluid End Market Valuation).
Smart Monitoring Adoption
IoT-enabled fluid ends with vibration sensors achieve 92% failure prediction accuracy, as demonstrated by Halliburton’s HT400 systems. GD Energy’s VX series reduces unplanned downtime by 30% through real-time wear analytics (VX Fluid End | GD Energy Products).
Material Innovations
Advanced composites are transforming component durability:
- Vulcan’s V-Series™ Advanced Stainless extends service life to 6,000+ hours in Permian Basin applications
- Ceramic-ZrO₂ liners demonstrate 3x wear resistance versus bimetal designs in abrasive slurries (Ceramic基复合材料烧结:工业软件国有化在孔隙率控制仿真中的替代)
- Nickel alloy hybrids withstand H₂S concentrations up to 15% in offshore sour gas fields
Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region (13.8% CAGR), fueled by:
- China’s shale gas production doubling to 60 Bcm by 2027
- Indian OEMs localizing 45% of fluid end components
- Southeast Asian offshore investments reaching $4.2 billion annually (Fracking Fluid End Market- Analysis and Forecast (2025-2032))
Conclusion and Recommendations
Summary of Key Points
This report has comprehensively analyzed fluid end parts across technological, market, and competitive dimensions. Key findings include:
- Material Innovations: Advanced materials like Vulcan V-Series™ Advanced Stainless (2,800 MTBF) and ceramic-ZrO₂ liners (6,000+ service hours) are redefining durability standards in extreme conditions (Ceramic基复合材料烧结:工业软件国有化在孔隙率控制仿真中的替代).
- Market Dynamics: The hydraulic fracturing fluid end segment is projected to reach $1.2 billion by 2030, driven by shale gas resurgence and high-pressure pump upgrades (Hydraulic Fracturing Fluid End Market Valuation).
- Regional Growth: Asia-Pacific emerges as the fastest-growing region (13.8% CAGR), fueled by China’s shale gas production doubling to 60 Bcm by 2027 (Fracking Fluid End Market- Analysis and Forecast (2025-2032)).
- Competitive Landscape: Top players like Weir Group and Gardner Denver dominate through modular designs and IoT-enabled monitoring, while Chinese OEMs leverage cost advantages with 40% lower-priced bimetal liners (BPMCO Fluid End Modules Accessories).
Final Thoughts
Fluid end parts are pivotal to industrial fluid handling systems, with their performance directly impacting operational efficiency and safety. The industry is undergoing a paradigm shift driven by:
- Smart Technologies: Halliburton’s HT400 sensors achieve 92% failure prediction accuracy, reducing unplanned downtime by 30% (Halliburton HT400 Plunger Pump Fluid End Assembly Parts).
- Sustainability Pressures: Stricter EPA regulations mandate 30% CO₂ reduction in forging processes by 2027, accelerating adoption of eco-friendly alloys (Fracking Fluid End Market- Analysis and Forecast (2025-2032)).
Future advancements will likely focus on hybrid materials (e.g., nickel-ceramic composites) and decentralized predictive maintenance systems, as seen in IoT-enabled fluid ends from GD Energy (VX Fluid End | GD Energy Products).
Recommendations
For Manufacturers:
- Invest in Smart Monitoring: Deploy integrated sensors (e.g., vibration, temperature) to enable predictive maintenance, leveraging platforms like PreMaint for real-time analytics (智能传感器在预测性维护中的应用研究-剖析洞察).
- Localize Supply Chains: Partner with Asian foundries to reduce lead times and costs, as demonstrated by Halliburton’s 40% production localization in China.
For Operators:
- Adopt Modular Designs: Standardized 8-bolt flange systems (e.g., Weir Novatech) cut replacement time to 90 minutes, minimizing field downtime (SPM Fluid Ends – SPM Oil & Gas).
- Prioritize Stainless Steel Ends: For sour gas environments, Vulcan’s Advanced Stainless™ extends service life by 50% versus carbon steel (Fluid Ends – Vulcan Industrial).
For Investors:
- Target aftermarket segments ($780 million by 2030) and Asia-Pacific markets, where Indian OEMs are localizing 45% of components (Fluid Ends Market Report | Global Forecast From 2025 To 2033).
These strategies align with the industry’s trajectory toward resilience, efficiency, and sustainability.







